What’s baffling about recent Mindanao quakes
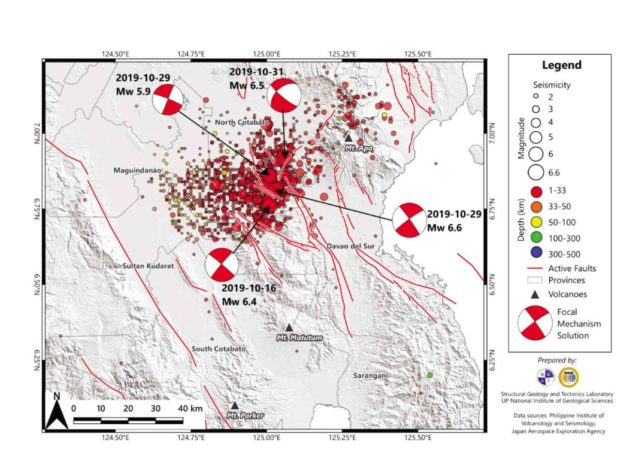
During an earthquake, theory dictates that aftershocks that follow the main shock should be of lower magnitudes. Further, there would be expected one first-level aftershock, 10 second-level aftershocks, a hundred third-level aftershocks, and so on. Stress releaseIn recent years, earthquake scientists have employed the principles of the Coulomb stress transfer (CST) theory to explain the behavior of seismic events. In some earthquakes, fault slippage may occur in two or more stages, producing multiple main shocks called doublet earthquakes. These data sets are now being used to assist a UP-NIGS geological team find the trace of a possible ground surface rupture.
Source: Philippine Daily Inquirer November 09, 2019 21:10 UTC







